Essential Resources for
Security Leaders
INTEL REPORT

MAX Intelligence: US-China Tensions to Rise Over Green Tech Product Tariffs
September 2024
This report covers the September 2024 tariffs on Chinese green technology products, analyzing the reasons and potential supply chain disruptions amid US-China trade tensions.
INTEL REPORT
MAX Intelligence: US Election 2024 Special Report
August 2024
This report covers the Democratic National Convention (DNC) on August 19-22, 2024, analyzing key speeches, policy shifts, and election strategies.
INTEL REPORT

MAX Intelligence: Venezuela Analysis
July 2024
Maduro’s likely victory in Venezuela’s July 28th elections could trigger unrest, with opposition claims of fraud threatening to destabilize the region.
INTEL REPORT

MAX Intelligence: MENA Analysis
July 2024
This report analyzes the UAV strikes in Tel Aviv on July 18-19, their link to Iran-backed factions, and the implications for regional stability.
INTEL REPORT
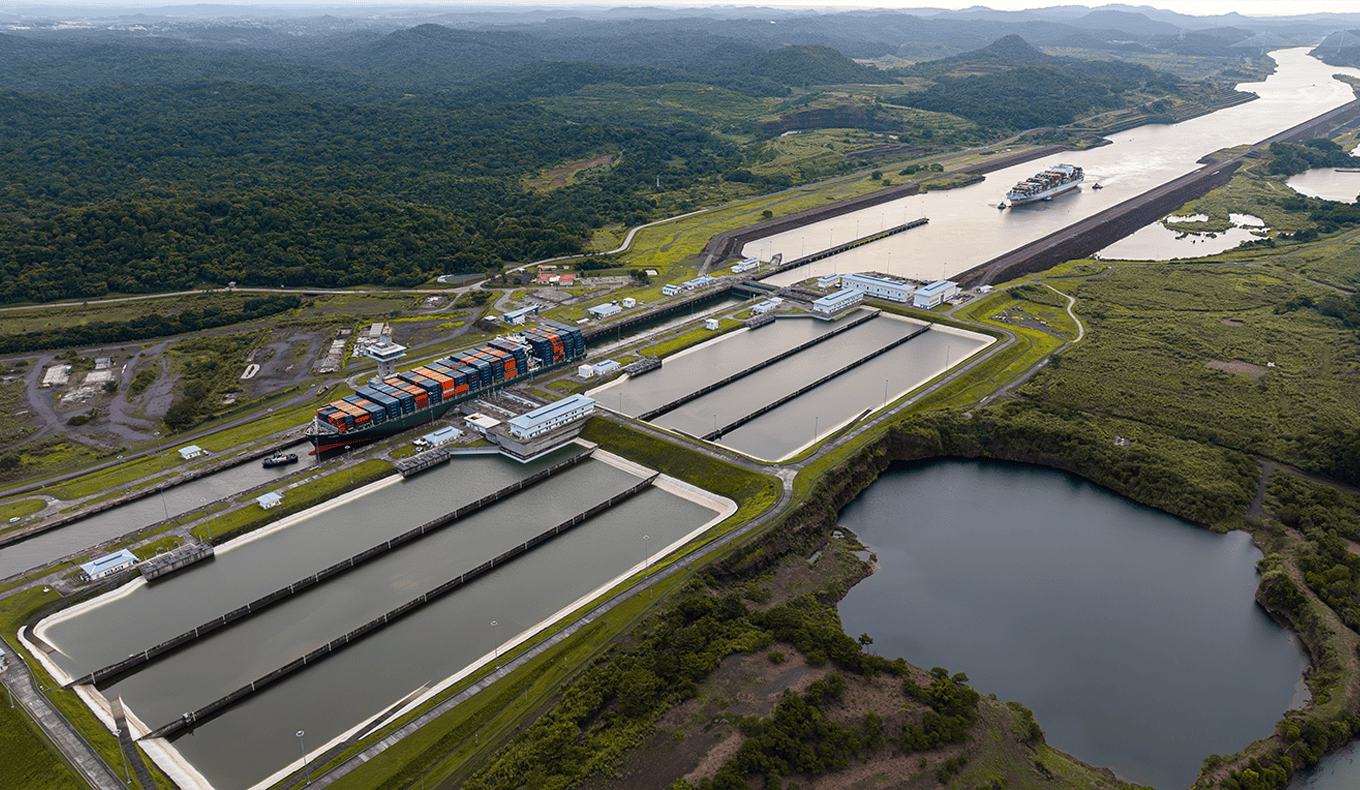

MAX Intelligence: Panama Canal Disruptions
July 2024
This report details how 2023 droughts disrupted Panama Canal operations, impacted global shipping, and the measures taken to mitigate future risks.
INTEL REPORT
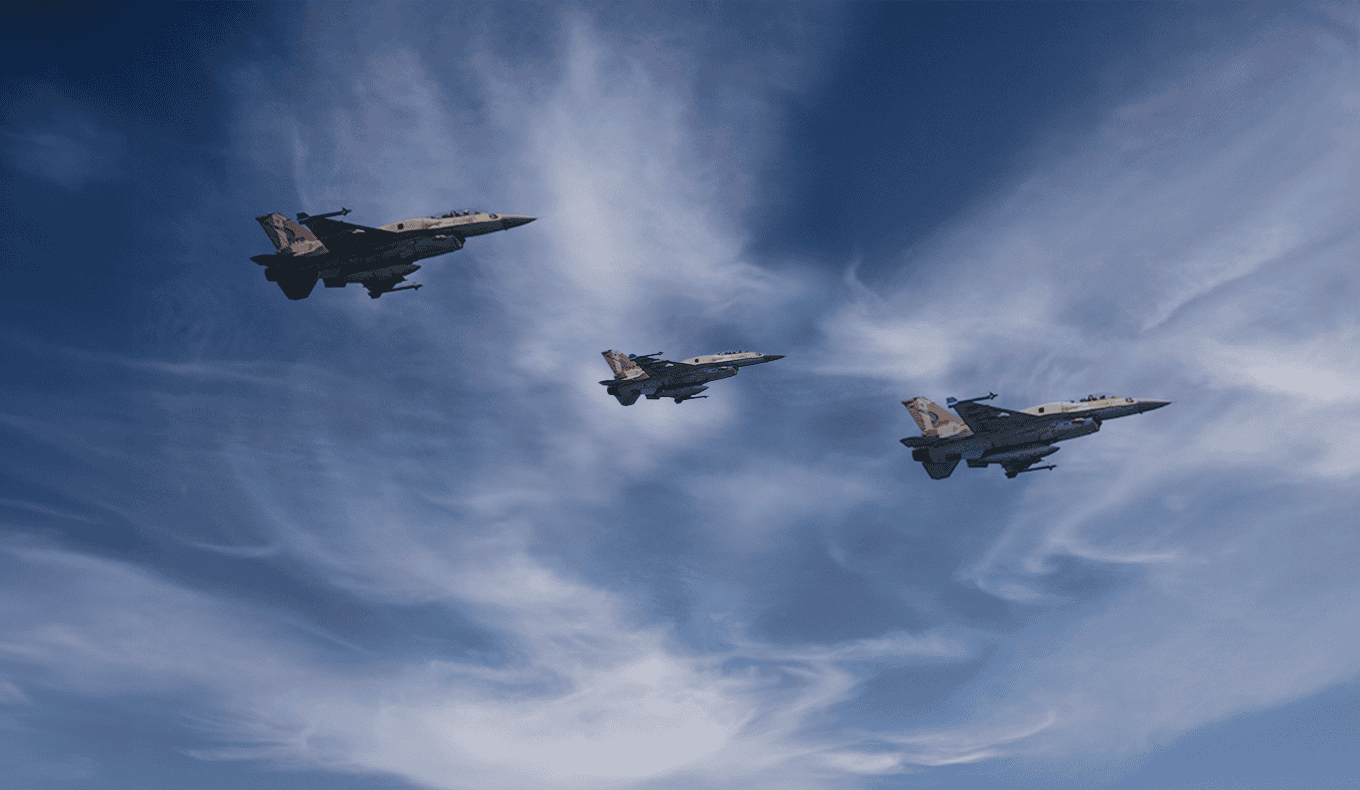

Critical Escalation: Yemen-Israel Conflict
July 2024
IDF’s July 20 ‘Outstretched Arm’ signals readiness to use force if red lines are crossed; Houthis likely to retaliate, though with limited success.
INTEL REPORT
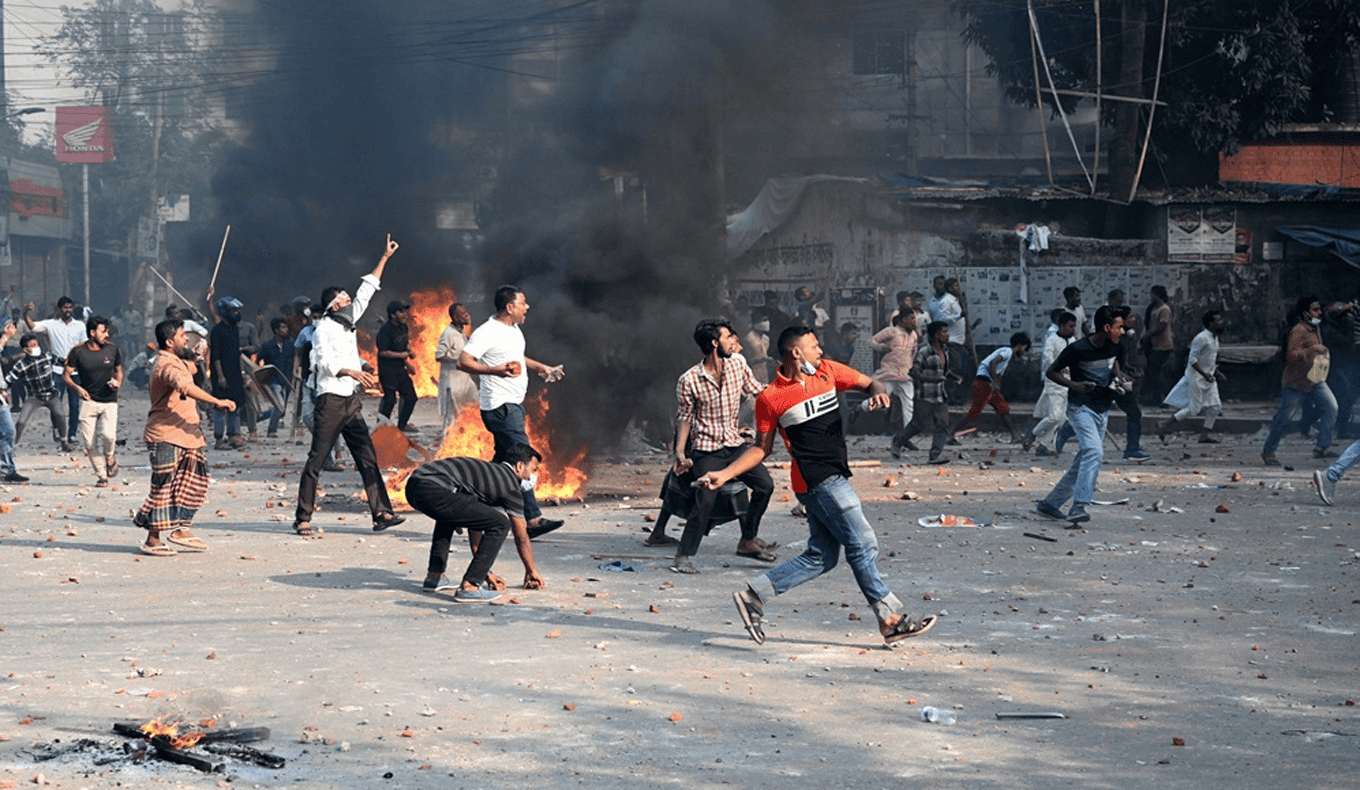

MAX Security: Bangladesh Analysis
July 2024
Violent student protests signal broader discontent with government, economy; business, travel disruptions likely over coming weeks.
IT’S A TOUGH WORLD