This report was written by Sanjana Parashar (MENA Intelligence Manager) and Swathi Nagesh (Levant region specialist)
And reviewed by Darren Cohen (MENA Senior Intelligence Manager and Levant region specialist) and Oded Berkowitz (Deputy Chief Intelligence Officer)
Executive Summary
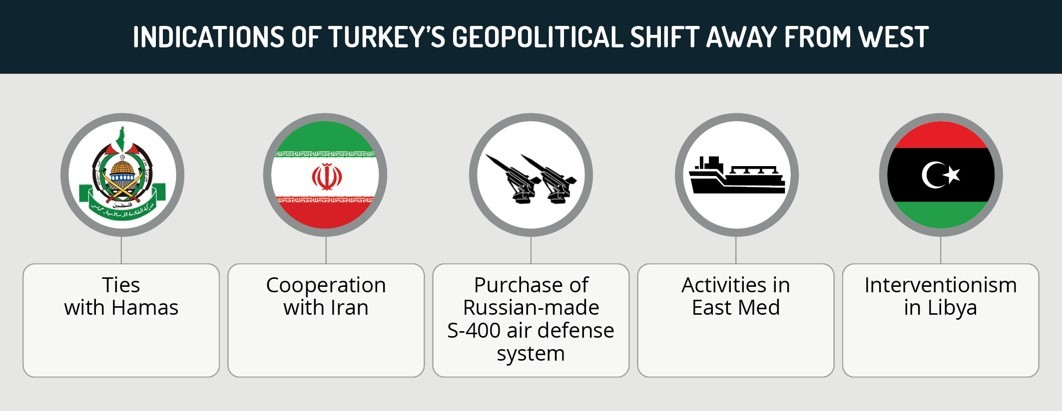
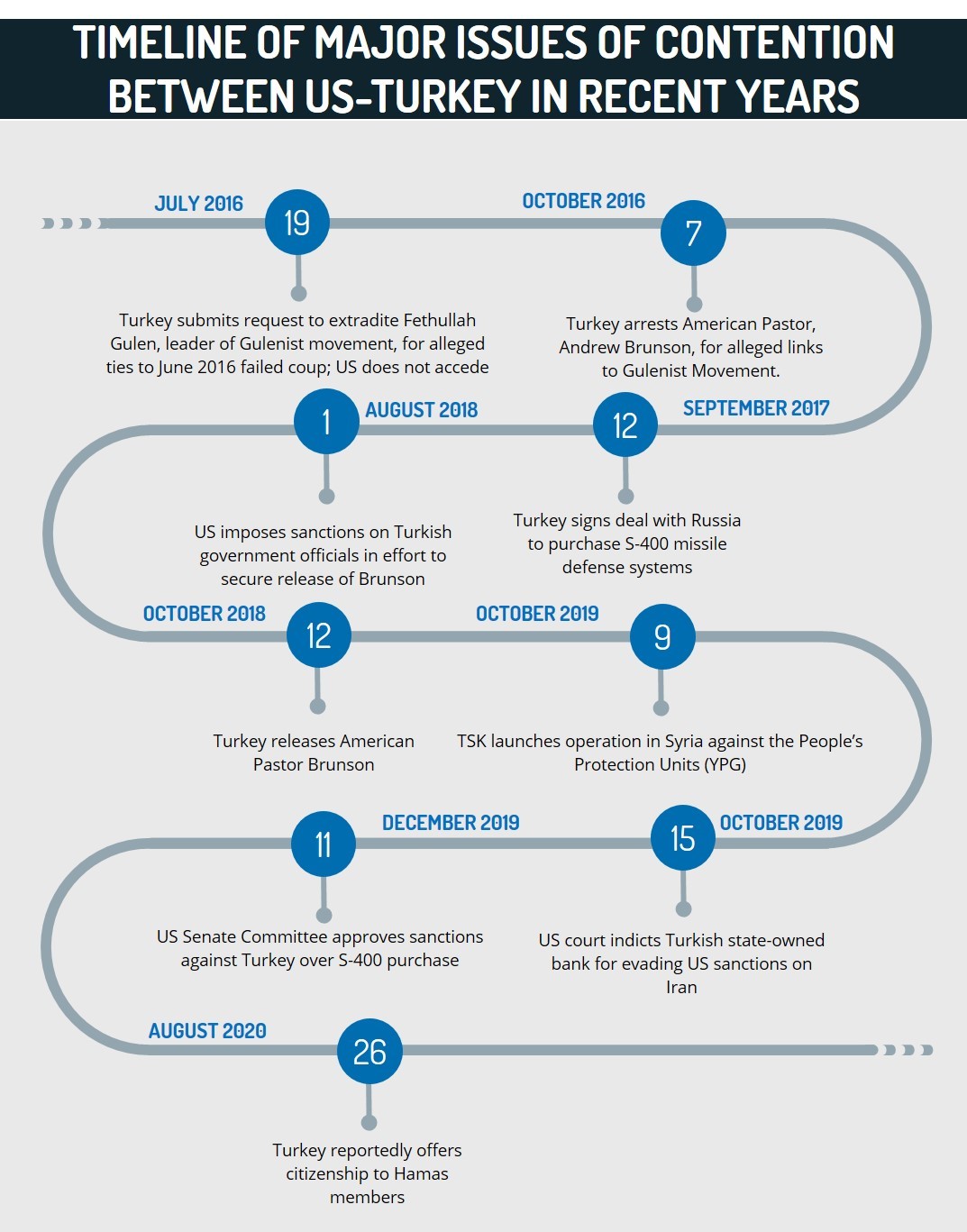
Tensions between Turkey and Western state actors have increased over recent years due to various geopolitical and security issues. Ankara’s pursuit of an independent foreign policy and the shift in its strategic alliances is the result of both developments in the domestic political sphere and the waning presence of leading Western actors in the region.
A significant area of contention is Ankara’s military interventionism. On October 8, the US condemned Turkey’s operations in Syria as posing “an extraordinary threat” to Washington’s national security. On October 5, Canada announced the suspension of arms exports to Turkey over Ankara’s reported military support for Azerbaijan in its conflict with Armenia. On September 21, the EU sanctioned a Turkish firm for breaching the UN arms embargo on Libya
These developments highlight the clash between Turkey’s effort to bolster its regional influence and secure its independent interests on one hand and the interests of its traditional Western partners on the other.
Turkey and the US have particularly disputed the former’s purchase of the Russian S-400 air defense system, which the latter contends threatens its advanced aerial capabilities. This decision reflects Ankara’s intent to overtly confront Washington and NATO by presenting its willingness to partner with Russia amid its broader efforts to bolster its regional authority.
Ankara’s efforts to gain accession to the EU over the past decades have suffered several setbacks over recent years as Brussels has condemned Turkey’s economic policies and alleged human rights violations. More recently, tensions have been elevated over Ankara’s deployment of research vessels to conduct oil and gas exploration activities in disputed areas of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea that are also claimed by Greece and Cyprus.
Furthermore, Turkey has been engaged in a diplomatic rift with France over perceived anti-Islam comments made by French President Emmanuel Macron. The dispute has added to a growing perception in the West that Turkey seeks to adopt a “neo-Ottoman” ideology and present itself as the “protector of Islam”.
While Ankara’s foreign policy decisions have primarily been driven by an effort to advance its independent geopolitical interests rather than ideological opposition to the West, these decisions will nonetheless serve to alienate the latter.
That said, Turkey’s economic interests are likely to override any other considerations and, therefore, Ankara will refrain from completely jeopardizing its ability to improve trade relations with Western countries as access to these markets is crucial to sustaining the Turkish economy.
Regardless, during episodes of elevated tensions between Turkey and Western-aligned states, the existing religious and nationalist zeal of segments of the local populace can potentially translate into a hostile atmosphere, including calls for boycotts of foreign goods, demonstrations, and aggressive rhetoric.
Western nationals conducting travel in Turkey are generally advised to maintain a low profile and exercise heightened vigilance in the vicinity of locales frequented by foreign nationals.
Assessments & Forecast
Turkey’s geopolitical shift is partly a product of developments within its domestic sphere, US’s waning presence in the region
Although the President Recep Tayyip Erdogan-led Justice and Development Party (AKP) won the 2018 general elections with a clear majority, the government’s popularity has somewhat decreased over recent years, as evidenced by the AKP’s losses in the 2019 municipal elections in Ankara, Istanbul, and Izmir. This is primarily due to the inability of the government to stabilize the economy, characterized by a significant devaluation of the Turkish lira since 2018. Furthermore, a broad crackdown on opposition actors and perceived dissidents has exacerbated existing anti-government sentiments of certain sections of the local populace. Against this backdrop, Ankara’s willingness to confront its Western allies is likely part of an effort to gain patriotic support for Turkey’s endeavors and project its regional dominance, which, in turn, is partly aimed at containing domestic criticism against the government.
Erdogan has also attempted to revive the legacy of the Ottoman Empire and use Islamic sentiments to consolidate power, particularly from conservative and Islamist-leaning members of the populace. This is evidenced by the July 10 announcement to convert Istanbul’s Hagia Sophia, designated a museum by Turkish secular leaders in 1935, into a mosque. Although the decision sparked condemnation by various international actors, Erdogan received support for the move from conservative Turks who make up part of his support base. The decision’s timing was thus partly an attempt to bolster Erdogan’s “strongman” persona while diverting the local populace’s attention away from Turkey’s deteriorating economic conditions, which have been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
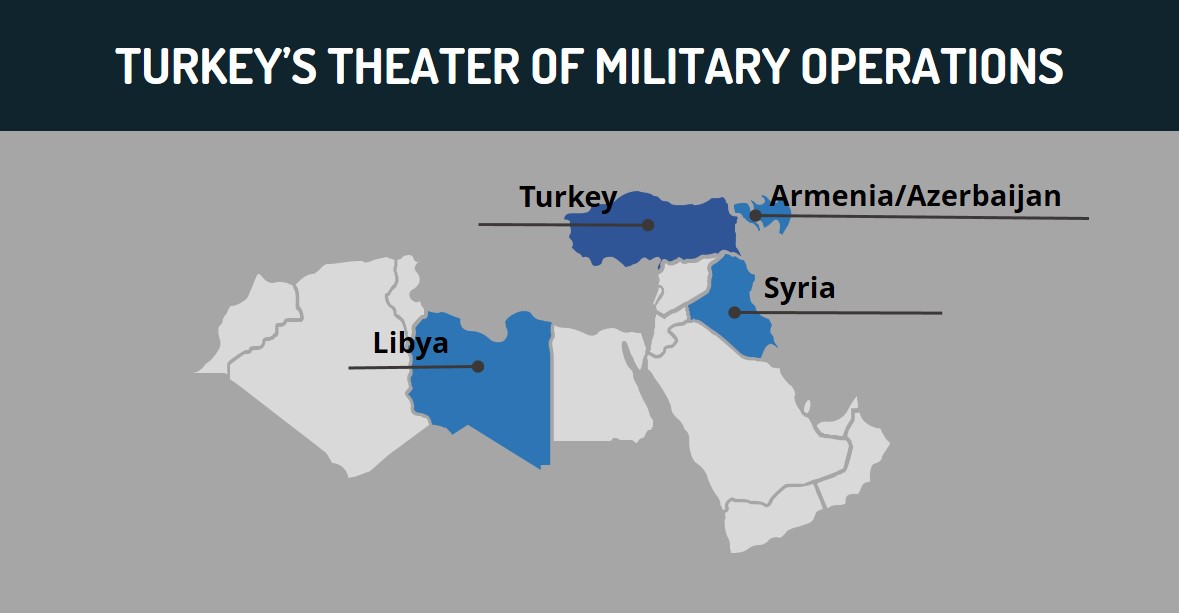
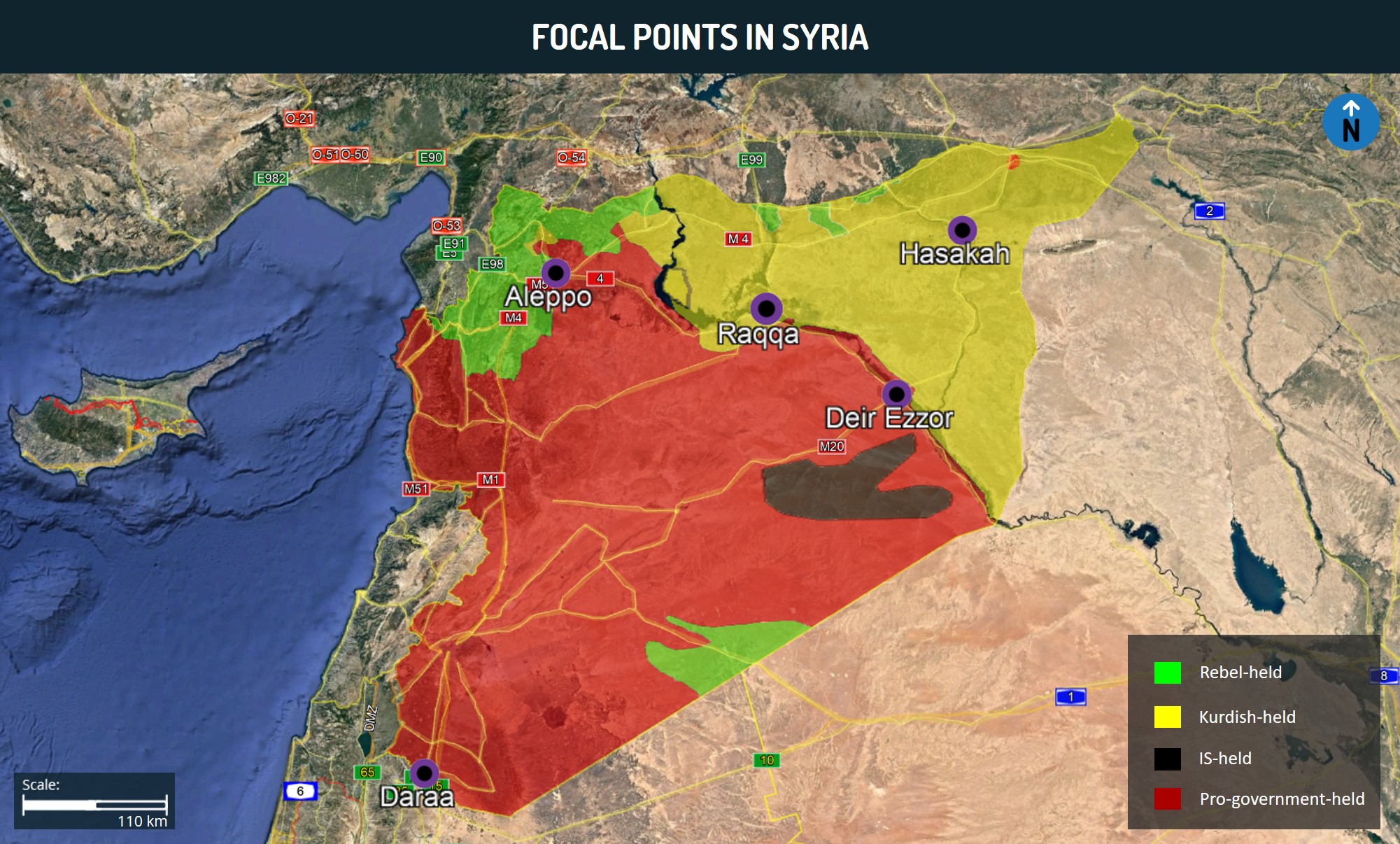
Meanwhile, Turkey’s growing military interventionism can also be partially attributed to the US’s waning presence in the broader region. Turkey’s Operation “Peace Spring”, aimed at dislodging Kurdish People’s Protection Units (YPG) militants from the area, was launched two days after the US’s October 7, 2019 announcement regarding the partial withdrawal of its troops from Syria. Turkey likely aimed to capitalize on this power vacuum to increase its influence within Syria and mitigate the Kurdish militant threat emanating from the country. Washington has also been largely uninvolved in Libya over recent years, which has allowed Turkey to become the main supporter of the UN-backed Government of National Accord (GNA) and therefore become one of the primary international actors involved in the country. Overall, the lack of military presence by Western state actors in these countries over recent years has created a relative power vacuum that Ankara aims to fill as part of its aspirations to expand its regional influence.
Turkey’s regional interventionism largely motivated by the pursuit of independent foreign policy, rather than ideological hostility towards West
In recent years, Turkey has pursued a more independent foreign policy, distinct from its traditional Western allies, as illustrated by its military regional interventionism, the acquisition of Russia’s S-400 air defense systems, and Ankara’s activity in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea that has led to tensions with EU states. This approach has been perceived by Western actors to be destabilizing and contrary to the West’s interests. However, this is primarily, although not solely, an effort by Ankara to establish a more dominant role in the region, rather than being motivated by an ideological hostility to the West.
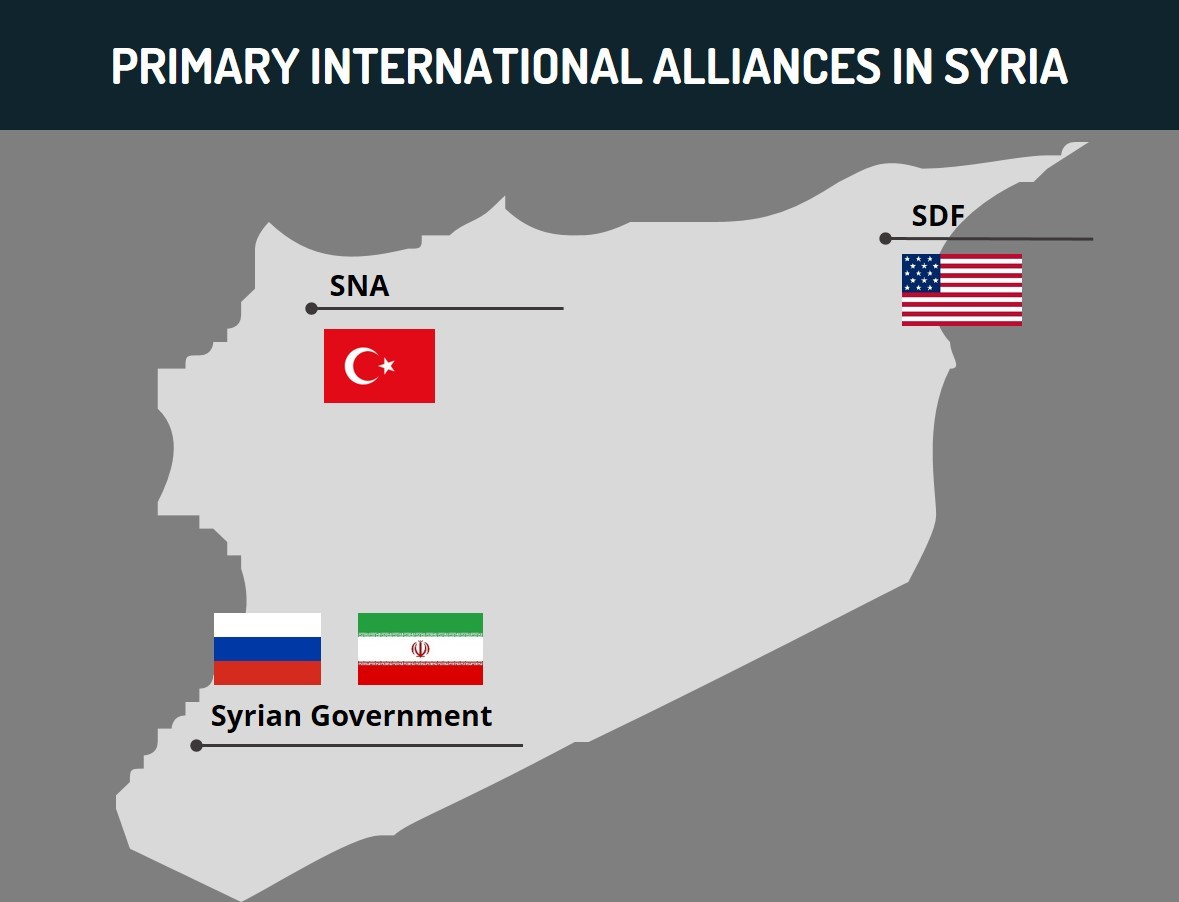
In Syria, Turkey’s efforts to mitigate what it perceives as the “Kurdish threat” to its national integrity have manifested in opposition to Washington’s interests. While Operation “Peace Spring” was launched primarily as an effort by Ankara to address the Kurdish militant threat, given the US’s alliance with the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), largely composed of the YPG, it collided with Washington’s interests in the country. Tensions over this issue have persisted over the past year, as evidenced by a statement published by the US on October 8 indicating that Turkey’s operations in northern Syria directly undermine the former’s anti-Islamic State (IS) campaign and US’s national security. Therefore, while Turkey’s policy was not directly motivated by an anti-US agenda, it nonetheless contributed to the growing rift between the two counties.
Also in the Syrian context, Turkey backs the Syrian National Army (SNA) rebel alliance, which opposes the Damascus government, backed by both Iran and Russia, all of whom are adversaries of the US. However, the leaders of Iran, Turkey, and Russia have led the Astana Peace Process for Syria, which was originally launched in January 2017, and largely reflects an effort by Ankara, as well as Tehran and Moscow, to project itself as a regional power broker. It particularly underscores Turkey’s willingness to cooperate with its rivals in the Syrian sphere in order to cement itself in the political processes that determine Syria’s future and therefore maintain a strong influence in the country, which it considers essential to its security interests. However, as Turkey strengthens its strategic partnerships with Iran and Russia, and thus develops a greater alliance with the West’s foes, it partially reinforces its position as a non-Western-aligned state. This is also given the lack of involvement of the US in the Astana process, which showcases Ankara’s willingness to form interest-based alliances independent of its Western allies.
Turkey’s military backing for Azerbaijan amid its conflict with Armenia over the Nagorno-Karabakh region has further served to alienate Western-aligned allies. Ankara’s support for Baku is partly driven by its shared ethnic and cultural ties as well as historical antipathy towards Armenia. NATO, however, has called for the restoration of peace between both sides in the region, while Western states, such as Canada, have actively condemned Turkey’s reported military support for Azerbaijan. Hence, Turkey’s role in this conflict as part of its independent foreign policy interests serves to supersede its obligations to this Western security alliance. That said, Turkey’s reported deployment of Syrian rebels to fight in the Azerbaijan-Armenia conflict and overall support for Baku is also a sensitive issue for Russia, due in part to the perceived threat of Islamist spillover regions along Russia’s southern borders and Moscow’s long-term cooperation with Armenia. This, therefore, showcases Ankara’s efforts to prioritize its own geopolitical interests, even if they partially undermine its alliances with either the West or with Russia.
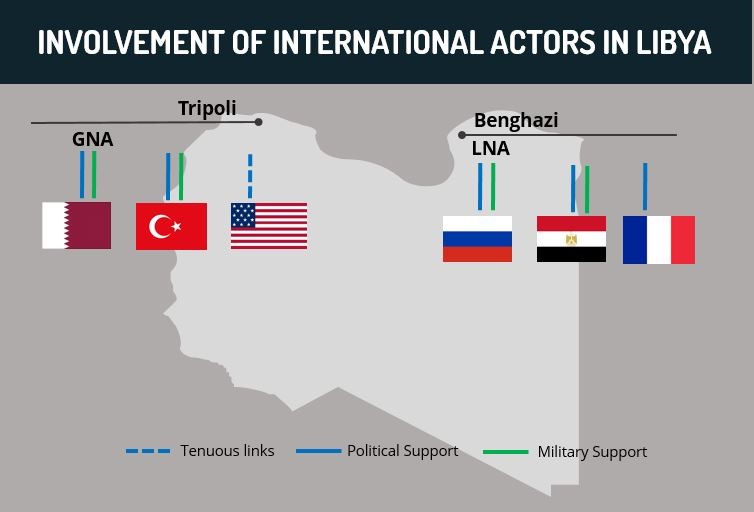
These opposing interests between Ankara and Moscow were also witnessed in Libya, where Turkey provides military support for Libya’s GNA and Moscow supports the GNA’s rival, the Libyan National Army (LNA). Amid Turkey’s increasing military reinforcements for the GNA, both in the form of equipment as well as Syrian fighters, Russia increased its provision of military equipment to the LNA as well as its deployment of Russian private military company (PMC) personnel. This further reiterates Turkey’s willingness to pursue its own military interests, potentially at the expense of the interests of its allies, both Western and non-Western.
Turkey’s acquisition of Russia’s S-400 reflective of efforts to confront the West, bolster its regional authority
Turkey’s acquisition of Russia’s S-400 anti-aircraft missile system, which the US has stated “cannot coexist with a Russian intelligence-collection platform that will be used to learn about its advanced capabilities”, is indicative of Ankara’s prioritization of its alliances with Moscow over its participation in the US’s F-35 program and its ties to NATO and the West. While Turkey insists that this does not clash with NATO assets or US F-35 aircraft, despite evidence to the contrary, pressure is growing in Washington to impose punitive measures on Turkey for its perceived transgressions. This was recently demonstrated by the US Senate Foreign Relations Committee’s condemnation of the S-400 testing, which the chairman called on October 16 “a direct threat to the [US-made] F-35”, adding that “US law requires sanctions against countries that continue to deepen their defense relationship with Russia.”
The decision thus reflects Ankara’s willingness to overtly confront Washington and NATO by presenting its conviction to partner with Russia amid its broader efforts to bolster its regional authority. In this way, Turkey aims to demonstrate that it is not bound by Western alliances and interests, which may in future grant it leverage over the West during potential disputes. Moreover, the decision is also likely rooted in domestic politics. By demonstrating Turkey’s willingness to acquire weaponry from any partner of its choice, Erdogan seeks to affirm Ankara’s sovereign right to choose its military alliances, regardless of the West’s objections. This, in turn, allows Erdogan to bolster his “strongman” credentials to the domestic audience.
As illustrated by Turkey’s recent testing of the S-400 system, regardless of concerns voiced by the US and other NATO members, Ankara is determined to proceed with the preparation process and ensure the systems become operational. FORECAST: Elements within the US foreign affairs establishment will continue to pressure the administration to sanction Turkey. However, US President Donald Trump’s reluctance to take action, as illustrated by the absence of sanctions despite the Senate’s approval of such measures in December 2019, renders it unlikely that imminent measures will be imposed. US policy vis-a-vis Turkey may change, however, if the presidential election yields a change in administration. This is unlikely to happen in the immediate coming months as it will take time for any administration to review and formulate its foreign policy.
Turkey’s ambitions to become a regional energy hub, secure foreign investments has also increased tensions with Western actors
Turkey’s involvement in Libya highlights its efforts to secure its energy interests in the region and counterbalance Greece, Egypt, Cyprus, and Israel. Turkey signed a Memoranda of Understanding (MoU) with Libya’s GNA on November 27, 2019 for this purpose. This includes the establishment of a maritime border between the parties and allows Turkey to stake a claim to oil drilling rights in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea, particularly in the vicinity of some Greek islands and the disputed waters south of Cyprus, which the Greek Cypriot administration claims is part of its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). The EU, particularly Italy, France, and Greece, as well as Egypt and Israel, have backed the Greek Cypriot government’s claim. Thus, although Turkey’s stance has elevated tensions with certain EU states and other regional stakeholders, Ankara’s determination to pursue its activities in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea highlights its willingness to take a confrontational stance against certain EU members to achieve its energy objectives.
This determination to enhance its energy security has likely also been bolstered by the actions of other regional actors in this context. On September 22, Egypt, Israel, the Palestinian Authority (PA), Greece, Cyprus, Italy, and Jordan established the East Mediterranean Gas Forum (EMGF) to promote natural gas exports from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Turkey was not included in the forum. Ankara’s Foreign Ministry spokesperson has reportedly stated that Turkey will “resolutely” continue to “protect its rights” in the Eastern Mediterranean and that “no alliance of malice” will prevent this. Ankara likely perceives the establishment of the EMGF as a provocative action aimed at actively excluding Turkey, which has likely increased its efforts to conduct exploration missions in the East Mediterranean. FORECAST: As illustrated by Turkey’s recent extension of the “Oruc Reis” research vessel’s activities in disputed waters until November 14, regardless of whether such action prompts tensions with the EU and potential sanctions against it in the framework of Brussels’ targeted sanctions program against Turkey for its “unauthorized” drilling activities of “hydrocarbons in the Eastern Mediterranean”, Ankara will persist with its exploration activities.
Meanwhile, Turkey and Russia have relatively divergent interests in the Black Sea. Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014 allowed it to expand its de-facto coastline to over a thousand kilometers, enabling the country to carry out its energy exploration, in direct conflict with the interests of NATO countries and their allies, such as Ukraine, in the Black Sea. In this context, on August 20, President Erdogan announced the discovery of a “320 billion” cubic meters gas reserve in the Black Sea, constituting the largest gas reserve discovered in the area by Turkey. Energy production from this reserve is slated to begin in 2023. FORECAST: Ankara’s discovery of a gas reserve in the Black Sea in August and its growing readiness to invest additional resources to carry out its exploratory missions in the area may increase Moscow’s perception that Ankara is attempting to impose itself in the region and thus increases the potential for friction with Russia.
Overall, both of these developments constitute an effort by Turkey to acquire energy security and thus reduce its dependence on other states to import oil and gas, which is likely becoming increasingly costly as the lira has devalued significantly over recent years. The fact that Turkey’s operations in both the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea have the potential to cause friction with both the EU and Russia again demonstrates that Turkey’s activities are part of an overall effort to implement an independent policy, and while liable to alienate its geopolitical alliances, do not constitute an explicitly anti-Western strategy. However, as illustrated throughout this report, regardless of whether Turkey aims to antagonize its Western allies, the outcome is ultimately the same.
Political rapprochement with US’s adversaries motivated by geopolitical concerns, desire to present itself as ‘protectors of Islam’, likely to further alienate West
In Turkey’s partnership with Iran, Ankara likely aims to counter what it perceives to be a growing regional threat to its ideology and interests. The Erdogan-led government seeks to impose its version of state-level political Islam, by forming alliances with Iran, Qatar, and Muslim Brotherhood groups and affiliates throughout the region. This is with the aim of countering the growing alliance of states in the region that it perceives as countering its interests and ideology, led by Saudi Arabia, Egypt, the UAE, all of whom are at least willing to collaborate with Israel and are largely acting in coordination with US interests. Thus, its increasing interventionism throughout the region can also be understood as an attempt to project Turkey as the “protectors of Islam” and has been perceived in the West as a form of “neo-Ottomanism” and an effort to invoke the spirit of the former Ottoman empire.
In this context, there has been a growing rapprochement between Iran and Turkey over recent years, in contrast with the ideological rivalry that initially emerged between the two states following the 2011 Arab Spring, with the parties largely on opposing sides in major conflict zones, such as Syria. The warming of their ties over recent years has manifested in political opposition to Saudi-aligned Gulf states and varying degrees of support for Qatar amid its rift with the former, both countries’ opposition to the “Abraham Accords” signed between Bahrain, the UAE, and Israel, as well as Iran’s diplomatic support for Libya’s Turkey-backed GNA. A recent September 8 meeting between President Erdogan and Iranian President Hassan Rouhani wherein they committed to conducting joint counter-militancy operations is thus indicative of increasingly cordial relations between the two states. FORECAST: These ties are liable to increase the tension between the US and Turkey, given the former’s efforts to diplomatically isolate Iran, as part of its broader “maximum pressure” campaign.
The ongoing rift between French President Macron and Turkish President Erdogan pertaining to the former’s defense of the right to draw caricatures of religious figures is likely to increase the West’s perception of Turkey “neo-Ottoman” aspirations. These diplomatic tensions followed the beheading of a teacher in France for showing caricatures of the Prophet Muhammad to his students and has generated a diplomatic fallout between Turkey and France, with Erdogan stating on October 24 that Macron should get “mental checks” and Macron on October 31 accusing Turkey of having a “bellicose attitude toward its NATO allies”, adding that Ankara has “imperial inclinations in the region”. The fact that this has also translated into anti-France protests throughout Turkey illustrates the impact of such diplomatic tensions and the potential for a hostile environment to emerge for Westerners operating in Turkey.
Meanwhile, the US has stated that it “strongly objects” to Erdogan’s hosting of the leaders of Hamas, the Palestinian militant group, in Turkey on August 22. The Turkish government announced that it “fully rejected” the US’s statement and accused Washington of “serving Israel’s interests”. Additional reports from August also indicate that Turkey is granting citizenship to Hamas operatives. Through this action, Turkey has signaled its willingness to legitimize the Palestinian militant group, as opposed to Washington’s categorization of the Gaza Strip-based group as a Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO).
Ankara’s actions are likely to be perceived by Western-aligned states as granting increased freedom of movement to Hamas and thus allowing them to carry out destabilizing activities in Israel. Similar to its relations with Iran, Turkey’s support for Hamas is unlikely to yield major economic or security benefits. Rather, it is indicative of an effort by Ankara to align with Muslim Brotherhood-affiliated and other Islamist groups and thus expand its sphere of influence throughout the region. Turkey also seeks to be a power broker and thus counteract recent ties between Gulf states and Israel, as evidenced by its hosting of talks between the two rival prominent Palestinian factions, Fatah and Hamas, for reconciliation talks on September 22.
These relations constitute a further fault line in the current tensions between the US and its allies on one side and Turkey on the other. FORECAST: Turkey’s growing support for Hamas as well as its opposition to Arab states’ normalization with Jerusalem, despite the fact Ankara maintains relations with Israel, is liable to increase tensions between the US and Turkey as well as Israel and Turkey. Although Jerusalem and Ankara share strong economic ties, Erdogan’s growing support for Hamas and persistent condemnations of Israel has the potential to strain these relations. This is particularly the case in light of the fact that Jerusalem now has formal ties with other regional states that are rivals of Turkey, primarily the UAE, and may therefore opt to cooperate economically with these countries, at Ankara’s expense.
Turkey to ultimately refrain from completely alienating its NATO allies
FORECAST: Taken as a whole, while Turkey is pursuing a more independent foreign policy, it is unlikely to completely alienate its Western allies, particularly NATO members. This is because Turkey can leverage its strategic position as a member of NATO to deter any significant punitive measures. This alliance also allows Turkey to mitigate the risk of direct confrontations as it implements its military policies in Syria, Libya, and Armenia/Azerbaijan, as well as within the energy sector, as Turkey pursues its energy interests in direct conflict with certain EU member states, such as Greece. In turn, despite the disputes between NATO member states and Ankara, Turkey will continue to remain a strategic ally by hosting US and NATO military assets, such as the Incirlik Air Base.
Within the context of the energy dispute between Turkey and the EU in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea, NATO also provides for peaceful dispute resolution mechanisms between its member states. This, therefore, allows NATO to mitigate the threat of direct confrontations between Turkey on one side and Greece and Cyprus on the other in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Hence, it is in the interest of NATO actors to continue to retain Turkey in the alliance as this would serve to manage emerging conflicts with EU members. This, in turn, provides Ankara with leeway in terms of its ability to pursue its energy policies without the threat of military confrontation with EU states.
Business continuity in Turkey for Western-linked entities unlikely to be significantly impacted, although potential punitive measures liable to elevate tensions
As previously mentioned, it is unlikely that under a President Trump administration, barring a breakdown in personal relations between the leaders, the White House will implement the Senate’s December 2019 approval of sanctions against Turkey. However, a Joe Biden-led presidency may seek to change course and punish states deemed to be acting in opposition to Washington’s core interests, for instance by operating Russian-made air defense systems.
In the event that the US imposes sanctions or tariffs, as in 2018, there is a high probability of further damage to the Turkish economy, as was witnessed following the implementation of such measures two years ago. This would lead to a further devaluation of the currency and render it more difficult for Turkish-based companies and Turkish state entities to remain competitive. FORECAST: Irrespective of who wins the US presidential election, as previously mentioned, any decision on sanctions or tariffs against Turkey is liable to take several months as the incoming administration formulates its foreign policy agenda. Regardless, Turkey’s actions may prompt other Western actors to consider punitive measures to pressure Ankara to alter its perceived destabilizing activities. This may, for instance, manifest in a ban on arms sales, as announced by Canada on October 5, which has the potential to undermine Turkey’s aforementioned defense strategy.
In the event that the US and/or the EU does impose sanctions or other punitive measures on Ankara, there is a potential for an increase in vocalized sentiment emanating from the government and domestic populace against the US, the West, or its perceived interests. This was illustrated by events in August 2018 amid the sanctions and tariffs imposed on Turkey by Washington, wherein a significant uptick in protests condemning the US was recorded in major cities in Turkey and President Erdogan reportedly called for a boycott of US electrical goods, while some Turkish citizens posted videos on social media of them physically attacking US-made products and currency.
Similarly, amid the aforementioned dispute over comments made by French President Macron regarding cartoons depicting the Prophet Mohammad, reports from October 26 indicate that Erdogan called for a boycott of French goods. Both of these episodes illustrate the existing religious and nationalist zeal of segments of the local populace that can translate into a potentially hostile atmosphere, including boycotts of foreign goods, demonstrations, and aggressive rhetoric. As per the prior example involving the US, these tensions tend to subside relatively quickly without a significant impact on foreign businesses operating in Turkey. However, there is also the potential for temporary retaliatory measures imposed by foreign states such as sanctions and tariffs, as occurred in 2018, as well as increased bureaucratic challenges for nationals of perceived adversaries, which may hinder operations in the country.
However, ultimately, Turkey’s economic interests are likely to override any other considerations. This is illustrated by its willingness to cooperate economically with China, despite differences in ideology. According to the EU, Turkey’s main export markets are the EU, the UK, the US, and Israel. Thus, despite Erdogan’s geopolitical activities, economic trade with its Western counterparts remains crucial for the stabilization and growth of the Turkish economy. FORECAST: The Turkish government is unlikely to significantly jeopardize its ability to improve trade relations with Western countries as access to these markets is crucial to sustaining the Turkish economy. Turkey’s geopolitical expansionism is therefore unlikely to have a significant impact on Western economic interests over the coming months. Moreover, Turkey is unlikely to place restrictions on private Western citizens or enterprises from operating in the country, even in the event of a dispute between the states in which these entities are based.
Recommendations
Travel to Istanbul, Ankara, and Izmir may continue while remaining cognizant of the latent threat of militancy, as well as regular anti-government protests and occasional incidents of unrest in these locales. Contact us at [email protected] or +44 20-3540-0434 for itinerary and contingency support options.
It is advised to avoid all travel to border areas with Syria and Iraq given the increased risk of militancy and spillover of armed conflict emanating from these countries.
Foreigners, particularly Westerners, conducting travel in Turkey are generally advised to maintain a low profile, and exercise heightened vigilance in the vicinity of locales frequented by foreign nationals. This is particularly the case in the event of elevated tensions between Turkey and Western or Western-affiliated states and entities.
Avoid any overt or critical statements of government, religious, or political institutions both in public spaces and online, including social media. It is also advised to be mindful of any social media posts made prior to travel that could be accessed publicly and could be viewed negatively during your visit. This is particularly the case during times of heightened political tensions involving Turkey in the international arena.