Current Situation
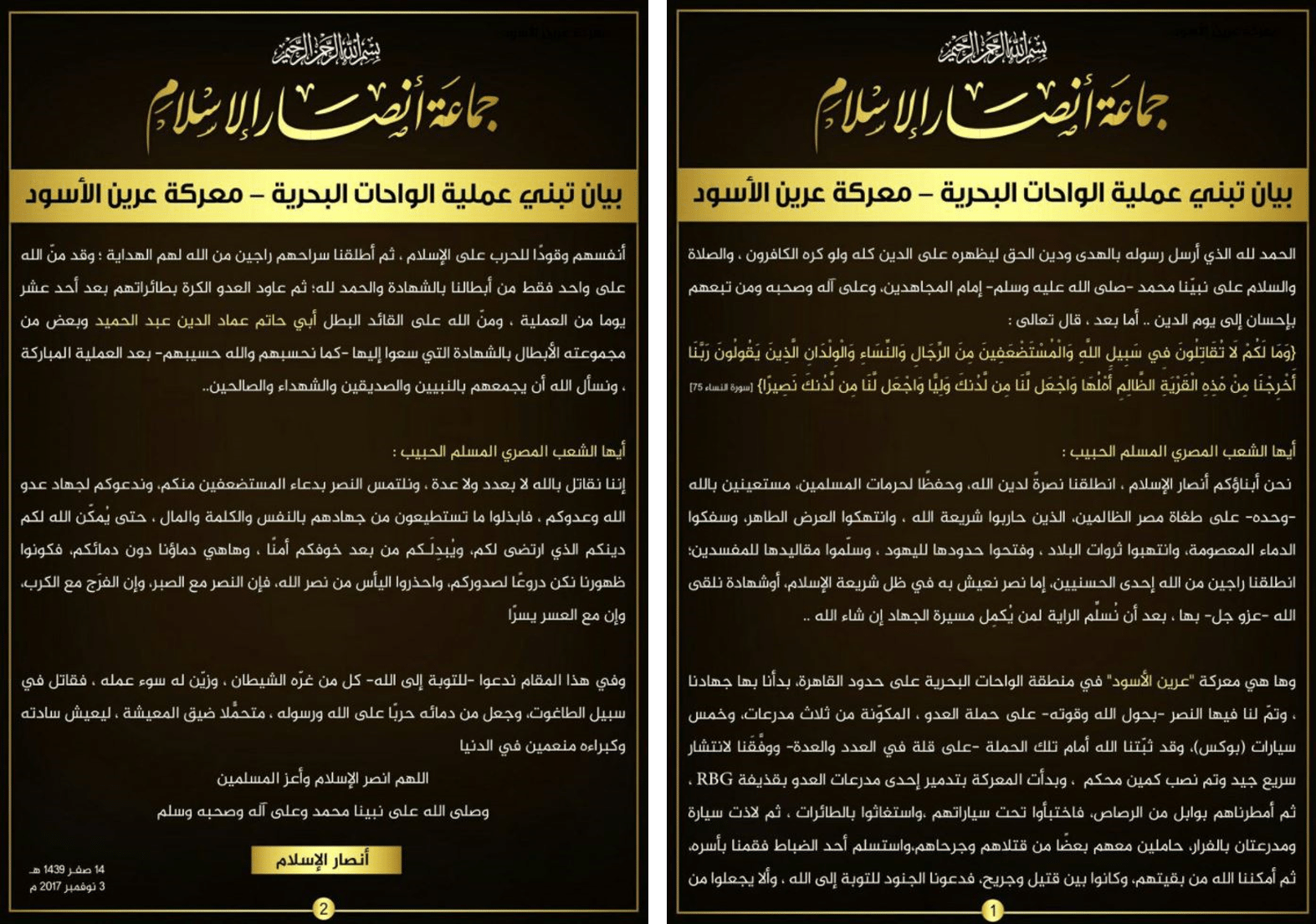
On November 3, a previously unknown militant group, Jamaat Ansar al-Islam, claimed responsibility for an October 20 attack in western Egypt’s Bahariya Oasis, in which reports state at least 55 security forces personnel were killed during a raid operation targeting a militant base.
In its claim of responsibility, the group introduces itself to the Egyptian public, denouncing Egyptian leadership for its treatment of the populace. The group states that the October 20 attack, which it describes in specific detail, marks the commencement of its “jihad” against government and military authorities in Egypt and proclaims itself to be a group that has exercised a “divine patience.”
The organization memorializes one of its leaders, Emad al-Din Ahmed, a former military officer who became a jihadist, who was killed during a counter-militancy operation on October 31, which included ground raids and airstrikes in a mountainous area near al-Wahat Road, west of Fayoum. Ahmed is reported to have been a deputy of Hesham al-Ashmawy, an al-Qaeda member reportedly operating in the eastern Libya city of Derna, who along with Ahmed had been forced from the Egyptian military’s ranks for professing alleged extremist Islamic beliefs.
The group stated that it freed security forces’ personnel who were kidnapped during the Bahariya Oasis attack, after lecturing them on the principles of Islam, and explaining that Egypt’s leadership is an enemy of the faith. Previous reports had stated that a police officer who had been kidnapped during the October 20 incident was freed during the October 31 operation.
The group appeals to the Egyptian public, asking the country’s citizens to provide Jamaat Ansar al-Islam with various types of support, urging them to join the group’s ranks, as well as sponsor the group financially.
Assessments & Forecast
While Jamaat Ansar al-Islam is a previously unknown group, the claim of responsibility for the attack is likely credible. Although the Islamic State (IS) maintains a significant presence in the Western Desert where the attack occurred, the organization did not claim the attack, even mentioning it in its monthly literature without taking credit for it. Jamaat Ansar al-Islam is widely reported as linked to al-Qaeda, and several indications support such an affiliation. Following the Bahariya Oasis incident, numerous al-Qaeda online profiles on jihadist channels publicized and praised the attack, while Ahmed’s reported association with the al-Qaeda-loyal Ashmawy would lend credence to the al-Qaeda affiliation. The claim of responsibility’s graphics and wording also resemble those of other al-Qaeda affiliates. Jamaat Ansar al-Islam’s announcement corresponds to al-Qaeda’s overall strategy of encouraging its affiliates to pursue local-specific goals, in this case to damage Egyptian leadership for its alleged mistreatment of Egypt’s population, as well as its perceived status as an enemy of Islam. IS, in contrast, targets these same interests, but rather for the purpose of destabilizing the state in order to advance the spread of an Islamic caliphate.
The emergence of an al-Qaeda affiliate in Egypt is highly notable in its own right, as the Sunni jihadist group has not maintained an active presence in the country in recent years. This group’s self-introduction comes amidst IS’s sustained territorial losses yielded in Syria and Iraq, where it only maintains control of a few swaths of land. Jamaat Ansar al-Islam likely chose to reveal its existence at this particular time to present itself an attractive alternative for IS fighters fleeing Syria and Iraq, as IS is increasingly seen as on the decline. The significant length of time that passed before Jamaat Ansar al-Islam claimed responsibility for the attack and unveiled itself as a group is likely due to communications difficulties with al-Qaeda’s central organization, particularly given the group’s presence in Egypt’s remote Western Desert, and that it is a new organization likely in the initial stages of establishing these contacts and communications capabilities. However, this could have been intentional, as the group may have waited to announce its existence to maintain a low profile and avoid drawing authorities’ attention and thus allow its militants to regroup.
As seen in the group’s eulogizing of one of its commanders who had been an officer in the Egyptian military, Ahmed most likely maintained connections with members of the military sympathetic to Islamist militancy, who given the success of the October 20 attack, likely informed the militants that the raid was to take place in advance. This would bolster our previous assessment that the militants likely had prior intelligence of the security operation’s launching from informants within the security forces. Furthermore, while the size of the group’s personnel has not been established as of yet, it displayed high capabilities during the Bahariya Oasis attack, which were likely enhanced by former military officers such as Ahmed. This was witnessed in the group’s strategically entrenched positions during the ambush, which included directing RPG and heavy gunfire from higher ground at both the front and rear of the security convoy, which significantly immobilized its personnel, as well as in the detonation of IEDs that followed. This complex multi-pronged attack, including the use of explosives, displayed high sophistication in both method and technical expertise, and the group’s remaining members likely retain these capabilities and knowledge.
Given Jamaat Ansar al-Islam’s likely affiliation with al-Qaeda, as well as its operations in Egypt’s Western Desert, the group most likely maintains ties with the Mujahideen Shura Council of Derna (MSCD), which is based across the border in Derna. The MSCD militia coalition’s largest faction, the Abu Salim Martyrs Brigade, is aligned with al-Qaeda. Jamaat al-Islam is likely to cooperate with the MSCD towards damaging shared enemies including Egyptian leadership, as well as Cairo’s Libyan ally, the Libyan National Army (LNA), whose dominion extends over much of eastern Libya. Such cooperation will likely include the exchange of weaponry and supplies across the border, as well as personnel on some occasions.
FORECAST: The group’s claim of responsibility will likely prompt a competition amongst militant groups operating in Egypt for manpower, prestige, and legitimacy. In response to Jamaat Ansar al-Islam’s announcement, IS and disenfranchised Muslim Brotherhood militant groups are now likely further motivated to conduct attacks in order to continue to convince Egyptians to join and support them rather than defect to this new organization, raising the potential for attacks in mainland Egypt at this this time. In terms of recruitment and manpower, Jamaat Ansar al-Islam’s call for jihadist-style militancy against Egyptian authorities would appeal to those in line with IS’s doctrine, while the specific local aims of the group to attack Egypt’s leadership for its alleged maltreatment of Egyptians would attract those of the Muslim Brotherhood ideology, including more radical elements part of groups such as the Hasam Movement and Liwaa al-Thawra. Al-Qaeda has also attempted in the past to establish such relationships with disenfranchised Muslim Brotherhood militants. Furthermore, Jamaat Ansar al-Islam likely utilized a recent downtick in activity by both IS and disenfranchised Muslim Brotherhood groups in mainland Egypt in recent weeks to portray itself as strong relative to these other organizations in an attempt to gain support.
FORECAST: In response, Egyptian authorities will prosecute further security raids and direct Egyptian Air Force (EAF) airstrikes targeting the group in Egypt’s Western Desert, aimed in part at preventing Jamaat Ansar al-Islam from strengthening itself through any cooperation with the MSCD and smugglers across the border in Libya. Towards this end, Cairo will likely heighten coordination with the LNA, and in some instances, as seen on May 26 and on a few occasions afterwards, will likely order EAF airstrikes against the MSCD in Derna. Furthermore, Egyptian authorities will seek to identify and arrest militant informers likely maintained by the new group within the military and security services. However, given the challenges inherent in policing the extensive Western Desert and its expansive international borders, Jamaat Ansar al-Islam will likely continue to operate there and will attempt to perpetrate further attacks. Furthermore, it remains possible that the group maintains personnel in other areas of Egypt, including in more heavily-populated areas in its interior cities, which would also be targeted by security forces.
Recommendations
Travel to Cairo and Alexandria may continue while adhering to all security precautions regarding militancy and civil unrest. Consult with us for itinerary-based travel recommendations.
Avoid all travel to the North Sinai Governorate and border areas with Libya, Sudan, and Israel due to the persistent risk for militant attacks, kidnappings, and general lawlessness.
In Cairo, maintain heightened vigilance and continue to allot extra time for travel due to possible delays emanating from increased security deployments, checkpoints, and closures throughout the capital.
As a general security precaution, remain vigilant in areas surrounding and avoid the immediate vicinity of government installations, police stations, and religious centers, particularly churches, as these locations remain under elevated threat of militant attacks. When traveling in central squares, or in areas with persistent police deployments, avoid the immediate vicinity of security forces, particularly fixed traffic booths, as such personnel and facilities have increasingly come under attack by militant elements.